- Email: info@crystalteck.com
- Location: Trichy
- Office Hours: 09:00 AM - 7:00 PM
iCrystal Inventory Management
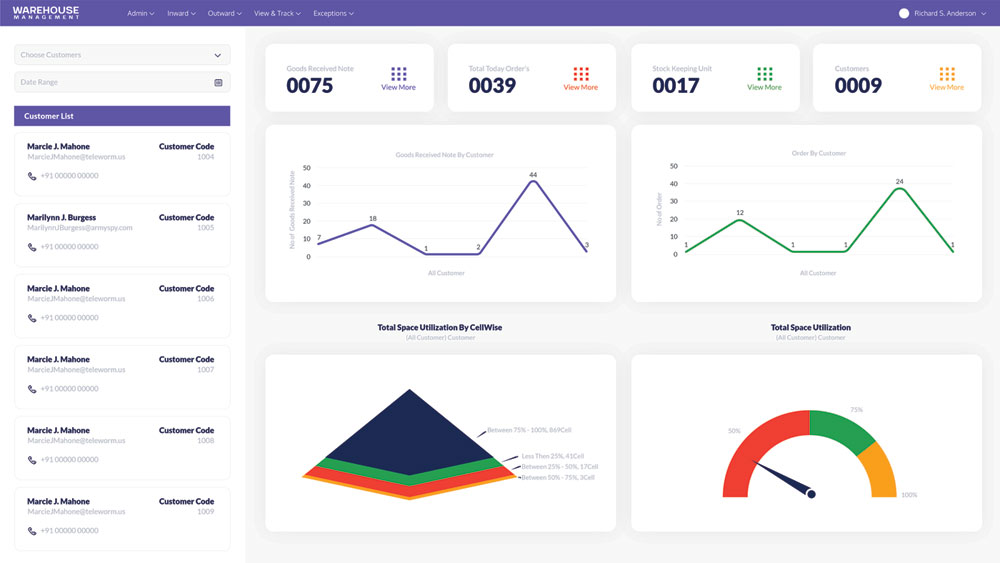
- Inventory Management modules in ERP systems are focused on tracking and controlling inventory levels across the organization.
- They provide tools for managing stock levels, tracking inventory movements (e.g., receiving, transfers, sales), optimizing reorder points and replenishment processes, and conducting inventory audits.
- Advanced Inventory Management features may include barcode scanning, serial number tracking, lot tracking, and integration with supply chain partners for real-time visibility into stock levels.
- Effective Inventory Management helps businesses minimize stockouts, reduce excess inventory carrying costs, improve order fulfillment accuracy, and streamline procurement processes.
Optimize, Organize, Outperform: Master Your Inventory with Us!
- Planning and Forecasting
- Procurement and Purchasing
- Receiving and Inspection
- Storage and Organization
- Tracking and Control
- Order Fulfillment and Shipping
Forecasting Demand: Predicting future demand for products based on historical data, market trends, and other factors.
Setting Inventory Levels: Determining optimal stock levels to meet customer demand while minimizing carrying costs and stockouts.
Vendor management: Selecting and managing relationships with suppliers to ensure timely delivery of goods.
Purchase Order Processing: Creating and managing purchase orders for acquiring inventory items.
Receiving Goods: Accepting deliveries from suppliers and inspecting them for accuracy and quality.
Inventory Reconciliation: Matching received goods with purchase orders and updating inventory records accordingly.
Warehousing: Storing inventory in appropriate locations within the warehouse, considering factors such as accessibility and safety.
Inventory Classification: Categorizing inventory items based on factors such as demand, value, and storage requirements.
Inventory Tracking: Monitoring the movement of inventory items within the organization, including transfers between locations and sales to customers.
Stock Counting: Conducting regular physical counts of inventory to reconcile with recorded quantities and identify discrepancies.
Order Processing: Receiving and processing customer orders, including picking, packing, and preparing items for shipment.
Shipping Logistics: Arranging transportation and logistics for delivering products to customers in a timely and cost-effective manner.
Key Aspects of Inventory Management
Inventory Offers
Inventory comprises goods and materials held by a business for resale or production purposes, including raw materials, work-in-progress, and finished goods.
Cost Considerations
Inventory costs include carrying costs (e.g., storage, insurance), ordering costs (e.g., processing, transportation), and stockout costs (e.g., lost sales, backorders).
Management Tasks
Inventory management involves planning, procurement, storage, tracking, and analysis of inventory levels to ensure optimal stock levels are maintained.
Control Techniques
Various techniques such as Just-in-Time (JIT), ABC analysis, and Economic Order Quantity (EOQ) are employed to control inventory levels and optimize costs.
Performance Measurement
Inventory turnover ratio measures how efficiently inventory is managed by comparing the cost of goods sold to the average inventory level to scale inventory task.
Importance
Effective inventory management is crucial for meeting customer demand, minimizing costs, optimizing operations, and maintaining competitiveness in the market.
Pain Points
- Overstocking and Understocking: Balancing inventory levels to meet customer demand while avoiding excess stock (which ties up capital and incurs storage costs) or stockouts (which lead to lost sales and customer dissatisfaction).
- Forecasting Accuracy: Difficulty in accurately predicting future demand for products, leading to inefficient inventory planning and procurement decisions.
- Inventory Tracking and Visibility: Lack of real-time visibility into inventory levels, locations, and movements across multiple warehouses or distribution centers, resulting in inaccuracies and inefficiencies in inventory management.
- Manual Processes and Data Entry: Reliance on manual methods for tasks such as data entry, inventory counts, and order processing, which are time-consuming, error-prone, and inhibit scalability.
- Inventory Optimization Challenges: Difficulty in optimizing inventory levels and assortments to align with changing market conditions, seasonal demand fluctuations, and evolving customer preferences.
- Supply Chain Disruptions: Disruptions in the supply chain, such as delays in shipments, quality issues with suppliers, or geopolitical events, can lead to disruptions in inventory availability and fulfillment.
- Obsolete and Slow-Moving Inventory: Accumulation of obsolete or slow-moving inventory, which ties up valuable warehouse space and capital, and may require costly write-offs or discounts to clear.
- Integration and Compatibility Issues: Challenges in integrating inventory management systems with other business systems (e.g., accounting, CRM) or compatibility issues with legacy software, leading to data silos and inefficiencies.
Why Inventory Management?
Customer Satisfication
Maintaining optimal inventory levels ensures that businesses can meet customer demand promptly, leading to higher satisfaction and loyalty.
Cost Control
Efficient inventory management helps minimize carrying costs and reduces the risk of overstocking or stockouts, resulting in significant cost savings.
Operational Efficiency
Streamlining inventory processes enhances overall operational efficiency by reducing errors, improving productivity, and freeing up resources for other tasks.
